The writer is an economist, anchor, geopolitical analyst and the President of All Pakistan Private Schools’ Federation
president@Pakistanprivateschools.com
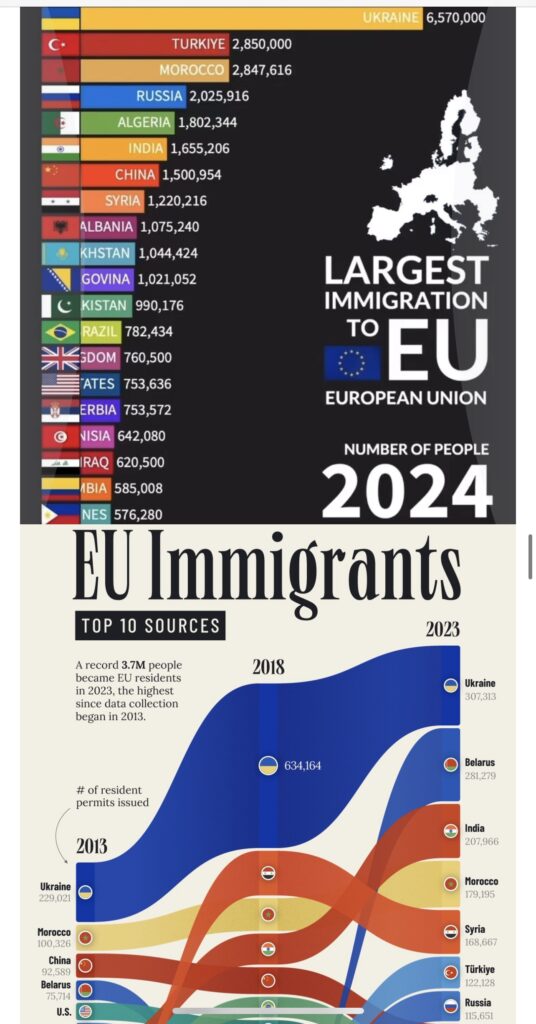
The demographic landscape of Europe is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by a surge in immigration from conflict-ridden countries. The root cause of this shift lies in the West’s own foreign policy decisions, specifically the military interventions and global war policies pursued by the US and EU in third-world countries. These actions have unleashed devastating conflicts, displacement, and human suffering, forcing millions to flee their homelands and seek refuge in Europe. The European Union has introduced a migration pact, “The European Union’s Migration Pact” is indeed a new era of Burden-Sharing requiring member states to receive migrants relocated from other countries. This pact aims to distribute asylum seekers more evenly across the EU, promoting burden-sharing and solidarity. The EU’s migration pact marks a significant shift in its approach to migration, emphasizing burden-sharing and solidarity. Effective implementation will be crucial to addressing Europe’s demographic challenges and harnessing the benefits of immigration. As, Europe is experiencing a significant demographic shift driven by increasing immigration. In 2023, 4.3 million people migrated to the EU from non-EU countries, while 1.5 million people previously residing in one EU country migrated to another EU country. Three Scenarios in demographic projections are important. High-Migration Case, assuming continued refugee inflows, Europe’s population is expected to grow significantly. Germany, for instance, has welcomed the largest number of Ukrainian refugees since February 2022, with over 1 million asylum seekers in 2024; Medium-Migration Case with moderate migration levels, Europe’s population growth will be steady. The EU’s population grew by 1.6 million people between January 2023 and January 2024, driven by post-COVID-19 migration and Ukrainian refugees; Low-Migration Case with reduced migration levels will lead to slower population growth. However, Europe’s aging population and low fertility rates will still require immigration to sustain economic growth. Demographic Implications are equally high: Age Structure in Immigrants are generally younger than the native population, contributing to Europe’s workforce and mitigating aging population challenges; Cultural Diversity is also Increasing immigration will enhance cultural diversity, with potential implications for social cohesion and integration; Economic Impact is also impacted, Immigration can drive economic growth, innovation, and entrepreneurship, but also poses challenges for labor markets and public services. Key Statistics shows that 59.9 million people in the EU were born outside their resident country (13.35% of the total EU population). Germany has the largest immigrant population (16.9 million), followed by France (11.9 million) and Spain (8.2 million). The EU’s population is projected to grow to 449.2 million by 2024, driven by migration. Europe’s growing immigrant population presents both opportunities and challenges. Policymakers must balance economic, social, and cultural considerations to ensure successful integration and harness the benefits of immigration. The EU’s migration pact marks a significant shift in its approach to migration, emphasizing burden-sharing and solidarity. Effective implementation will be crucial to addressing Europe’s demographic challenges and harnessing the benefits of immigration: Relocation Mechanism through member states will receive migrants based on a distribution key, considering factors like population, GDP, and asylum processing capacity; Mandatory Quotas of the countries will be required to accept a certain number of asylum seekers, with flexibility for those unable to meet quotas; Faster Processing of the pact aims to speed up asylum procedures, ensuring timely decisions and reducing processing times. The migration pact will influence Europe’s demographics, particularly in the context of growing immigrant populations. Three scenarios model the impact of migration levels: High-Migration Case will be continued refugee inflows will lead to significant population growth, with countries like Germany and Sweden experiencing increased diversity; Medium-Migration Case of moderate migration levels will drive steady population growth, with the EU’s population projected to reach 449.2 million by 2024; Low-Migration Case will reduced migration will result in slower population growth, emphasizing the need for immigration to sustain economic growth. But, the challenges and opportunities are equally important: Integration of the successful integration of migrants will be crucial, requiring investments in language training, education, and job placement; Strengthened border controls will be necessary to manage migration flows and prevent irregular migration; The pact’s success depends on member state solidarity, with countries working together to address migration challenges. The EU will implement the migration pact through: National Implementation Plans of member states will develop plans outlining their relocation strategies and capacity-building measures. The EU will provide funding to support member states in implementing the pact and integrating migrants. The EU will monitor progress, evaluating the pact’s effectiveness and making adjustments as needed.
As the continent grapples with the implications of this influx, it is imperative to acknowledge the causal link between Western military interventions and the resulting migration crisis. The high-migration scenario assumes continued refugee inflows, which will significantly alter Europe’s demographic makeup, posing both opportunities and challenges for social cohesion, economic growth, and cultural identity.
Geopolitical tensions on the influx of migrants from Africa, the Middle East, and Ukraine is straining EU relations with neighboring countries and exacerbating tensions with far-right groups. Europe is experiencing a significant demographic shift, driven by increasing immigration from conflict-ridden countries. The influx of migrants is largely attributed to Western military interventions and global war policies in third-world countries, which have led to devastating conflicts, displacement, and human suffering. The primary source countries of refugee flows into Europe, such as Syria, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Libya, have one thing in common: they have all been subject to Western military interventions, aimed at toppling dictators, promoting democracy, and fighting terrorism. These interventions have created a humanitarian crisis, with millions displaced, homes destroyed, and livelihoods obliterated. The high-migration scenario assumes continued refugee inflows, which will significantly alter Europe’s demographic landscape. The EU’s population is projected to grow, with countries like Germany, France, and Italy experiencing increased diversity. However, this shift also poses challenges for integration, social cohesion, and cultural identity. The migration crisis has significant geopolitical implications, including: Strained EU Relations the influx of migrants has strained EU relations with neighboring countries and exacerbated tensions with far-right groups; Europe’s migration policies will influence global migration patterns and shape international cooperation on migration issues; Effective migration management will contribute to regional stability, while mismanagement may exacerbate tensions and instability. Economic Impact on the immigration can mitigate Europe’s aging population and labor shortages, but also poses challenges for integration, housing, and public services. Europe’s growing immigrant population presents both opportunities and challenges. Effective management of migration, through regional collaboration and securitization, is crucial to addressing demographic shifts and ensuring economic growth. Assuming continued refugee inflows, Europe’s population is expected to grow significantly. Even in “no migration” scenarios, the share of the emigrants in the Europe’s population is still projected to rise modestly, showing how demographics alone can reshape societies over time. Germany, for instance, has welcomed the largest number of Ukrainian refugees since February 2022, with over 1 million asylum seekers in 2024. With moderate migration levels, Europe’s population growth will be steady. The EU’s population grew by 1.6 million people between January 2023 and January 2024, driven by post-COVID-19 migration and Ukrainian refugees. In the high-migration case—assuming continued refugee inflows like the 2015 peak—Sweden hits 30.6% and Germany 19.7% Muslim by 2050, driven by fertility rates and immigration. Real-world trends may differ as EU policies have tightened since then, potentially aligning closer to medium or zero-migration forecasts of 11-14% continent-wide. Western Europe sees higher shares due to historical migration hubs and policies, while Eastern Europe remains low from restrictive borders and minimal inflows. They’re estimates, not certainties—outcomes hinge on policy shifts, economic factors, and demographic trends; medium migration yields lower figures (e.g., France ~12.7%). Under high migration and sustained fertility gaps, emigrants shares could surpass 50% in Sweden, Austria, and Germany by 2100, approaching majorities across Western Europe by 2125 via compounded growth. This extrapolates the 2016-2050 pace, where shares roughly tripled in high-inflow nations. Yet, such forecasts hinge on unchanging policies; tightening borders, converging birth rates, and cultural shifts could halve these outcomes, as history shows demographic trends bend to decisions. Europe’s Muslim population growth isn’t also just due to migration about half of it comes from younger age demographics and higher birth rates within existing communities. The Role of Western Oceans in Addressing Human Trafficking and Irregular Migration. The Western Oceans play a critical role in addressing human trafficking and irregular migration. Regional organizations, such as the European Union, are promoting naval collaboration, harmonizing legal frameworks, and sharing intelligence to combat transnational maritime crimes. Through Securitization Theory which examines how non-traditional threats, like human trafficking and irregular migration, are framed as existential security issues. The EU’s migration pact, adopted in May 2024, aims to address these threats by screening asylum applicants at the point of entry and immediate deportation once the asylum claim has been denied. Regional Organizations’ Role in Promoting Naval Collaboration is equally important. Regional organizations, like the EU, are crucial in promoting naval collaboration and addressing maritime crimes. They: Harmonize Legal Frameworks by standardize laws and regulations to combat human trafficking and irregular migration; Share Intelligence through exchange information to identify and disrupt transnational maritime crime networks; Promote Naval Collaboration through the foster cooperation among member states to enhance maritime security and combat human trafficking. Europe’s growing immigrant population presents significant implications for global and regional geopolitics. It’s significance on the demographic SM shift through Immigration is remaking Europe’s demographic landscape, with far-reaching consequences for social cohesion, economic growth, and cultural identity. To address the migration crisis, the EU should: End military interventions and prioritize diplomacy, development, and humanitarian aid; Tackle the underlying causes of migration, such as conflict, poverty, and climate change; Invest in language training, education, and job placement programs to promote social cohesion and economic inclusion; Strengthen partnerships with origin and transit countries to address shared migration challenges. Comprehensive Migration Policy is needed that the EU should adopt a unified, flexible migration policy addressing asylum procedures, border control, and integration strategies. International Cooperation by strengthen partnerships with origin and transit countries to address root causes of migration, such as conflict, poverty, and climate change. Integration initiatives by investing in language training, education, and job placement programs to promote social cohesion and economic inclusion. Addressing Far-Right sentiment to encourage inclusive, evidence-based policymaking to counter far-right narratives and promote diversity. Regional collaboration to foster regional cooperation to address shared migration challenges, such as human trafficking and irregular migration. Global and Regional Implications on global migration trends in Europe’s migration policies will influence global migration patterns and shape international cooperation on migration issues. Regional Stability through effective migration management will contribute to regional stability, while mismanagement may exacerbate tensions and instability. EU enlargement through migration will impact EU enlargement, with candidate countries needing to align with EU migration policies. Europe’s growing immigrant population presents both opportunities and challenges. A comprehensive approach, addressing the root causes of migration and promoting integration, is crucial to managing the demographic shift and ensuring regional stability. As the continent grapples with the implications of this influx, it is imperative to acknowledge the causal link between Western military interventions and the resulting migration crisis. The high-migration scenario assumes continued refugee inflows, which will significantly alter Europe’s demographic makeup, posing both opportunities and challenges for social cohesion, economic growth, and cultural identity.